We've all been there. You try to log into your bank account with your username and Laruanpassword only to be met with a generic "incorrect password" error. You double-check your password manager, try a few variations, but after too many failed attempts, the system locks you out. Now you're funneled into a tedious re-authentication process involving security questions you barely remember and a password reset form that smugly informs you, "New password can't be the same as the old one." You proceed to throw your device in frustration.
A passkey is a secure, easy-to-use replacement for passwords. It uses your device's built-in security (like Face ID, fingerprint, or a PIN) to log you into a website or service, without requiring you to remember or type anything.
The passkey is then stored on a secure element of your phone or computer, which means the website or service you're accessing won't need to store any passwords on their servers – reducing the risk of breaches or hacks.
In practical terms, you could say passkeys merge the concept of a password and 2FA (two-factor authentication) into one smooth action, but way more secure and way less annoying.

As an optional and recommended step, you can store your passkeys inside a secure password manager such as Proton Pass, 1Password, Dashlane, or Bitwarden. This allows you to sync and access your passkeys across multiple devices.
Creating a passkey is easy, and the process is similar across most platforms. To illustrate, here's how we set up a passkey for Amazon.com and used a password manager to store it...
First, I log into my Amazon account and navigate to the Login & Security section to access the passkey option.

Next, I click on "Add a passkey," which creates a passkey specifically for Amazon. As shown in the screenshot, I had previously created a passkey that's stored in my iCloud Keychain. You can create multiple passkeys for the same website and store them in different places.

Because I use Proton Pass and I have their browser extension installed, adding a passkey automatically opens Proton Pass to generate and store it. If I didn't have Proton Pass installed, my web browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) would have stored the passkey instead.

Proton Pass will now save this specific passkey for Amazon, synced to my username. Since this is for Amazon, it also works for Amazon Web Services (AWS) accounts.
According to NordPass's research, the most popular password remains "123456" as of 2023 and 2024. The second most popular? "123456789." Other common passwords are usually strings of sequential numbers or variations on "qwerty." After six years of the same study, NordPass concludes that most people's password habits haven't meaningfully changed.
| Feature | Password + 2FA | Passkey |
|---|---|---|
| Steps | Multiple | Single |
| User needs to... | Type & wait | Just confirm |
| Security | Good | Better (phishing-resistant) |
| Convenience | Medium | High |
Passkeys are more secure because they eliminate password-based vulnerabilities, replacing passwords with cryptographic keys that protect users from phishing attacks, credential theft, and data breaches. Passkeys are protected by a single biometric factor, like your fingerprint or face, and no passwords are sent over the internet or stored on external servers.
While not every service has implemented passkey authentication, most popular sites have. Some of the major ones that support it include Amazon, Google, Apple, Github, Adobe, Uber, Microsoft, Nintendo, PlayStation Network, eBay, and Dropbox, as well as many social networks.
Financial institutions (banks) lag behind big tech giants in adopting passkeys, however companies like PayPal, Revolut and Robinhood already support it. Dashlane offers a helpful, community-driven directory of websites that have implemented passkeys login functionality.

You can already create passkeys using Google, Microsoft, or Apple devices. Many password managers – such as Proton Pass, Dashlane, 1Password, Bitwarden, and LastPass – also support passkey creation. As mentioned earlier, using a password manager allows passkeys to sync across devices.
It's also important to remember that passkeys are unique to each website. The passkey you use to sign into your Google account is not the same as the one used for Amazon. That said, a helpful pro tip is to create a passkey for your Google account and then use Google's authentication to sign in to other services (if the option exists). That way you can just use your one Google passkey while being able to access multiple websites.
Passkeys (technically known as Web Authentication or WebAuthn) are a technology that allows credentials to be authenticated without being stored on servers. They are part of the FIDO2 project, which aims to permanently replace passwords as a method of authentication.
The core concept relies on public key infrastructure (PKI). Instead of storing a username and password, passkeys are generated on an authenticator controlled by the user.
This authenticator could be your smartphone (Face ID, fingerprint), your operating system (e.g., Windows Hello), your browser, or a physical security key such as a YubiKey or Google's Titan Key.
Creating a passkey is a 3-step process:
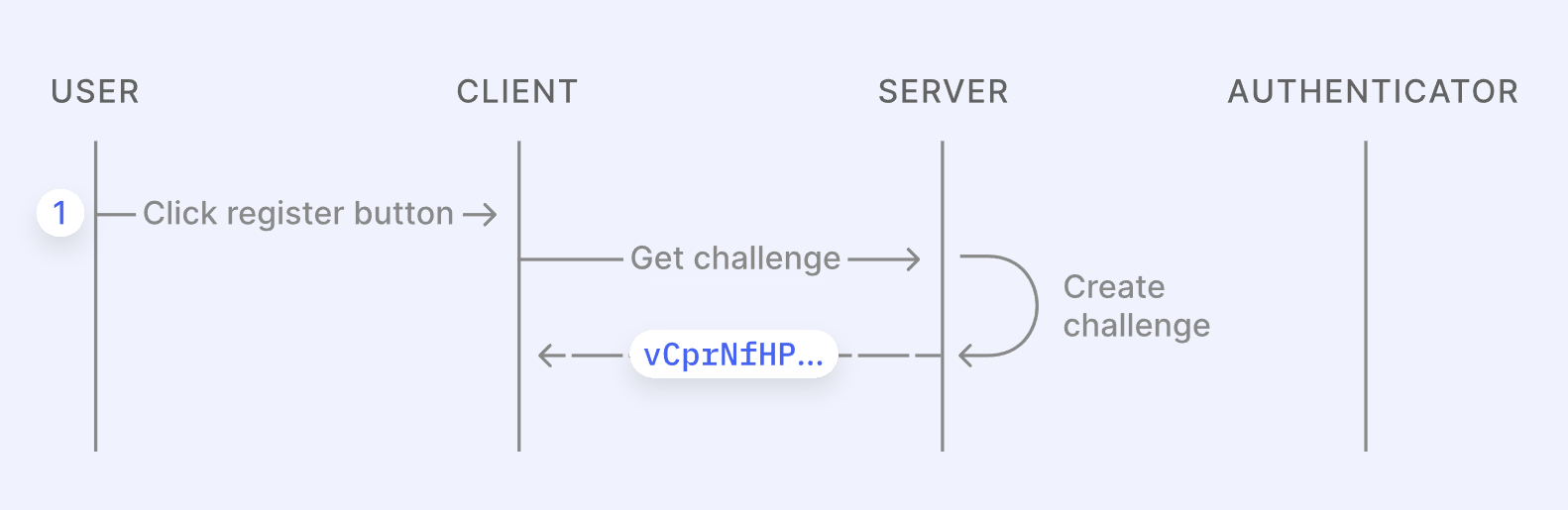
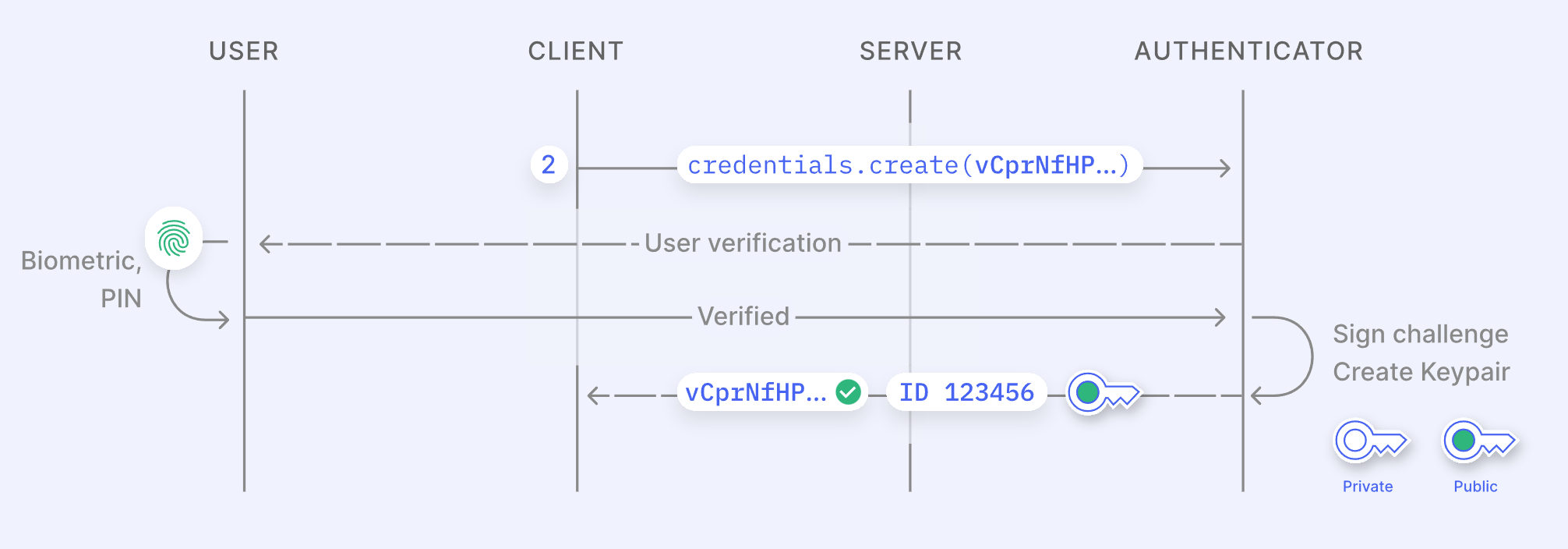
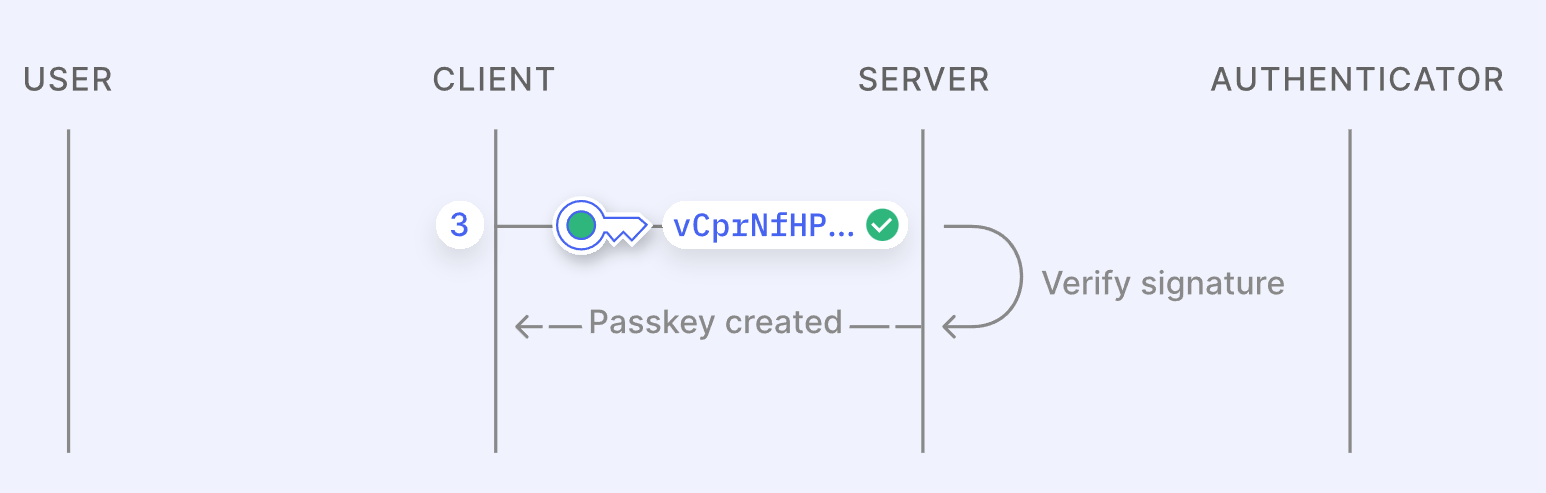
If you lose your device, your passkeys aren't lost – they're securely backed up in the cloud through services like Apple's iCloud or Google's Password Manager (or the password manager of your choice). These backups are end-to-end encrypted, meaning only you can access them, and they sync across your devices for easy recovery.
When you set up a new device, you can restore your passkeys simply by signing in to your cloud account. If you don't have another device, recovery options like a recovery key or multi-factor authentication can help you regain access.
Passkeys also require biometric authentication (like Face ID or a fingerprint) to use. Even if someone steals your phone, they can't access your passkeys without your biometric data.
Password managers are a good step up from remembering passwords, but they still rely on storing credentials on a server. Even open-source options like KeePass require a database of passwords. Even open-source tools like KeePass require you to maintain a password database.
Passkeys offer a more secure and streamlined approach by eliminating the need to manage individual logins. For the best of both worlds, we recommend using password managers alongside passkeys to ensure your credentials stay synced, backed up, and secure.
Absolutely. Phishing typically aims to steal usernames, passwords, or sensitive data. Passkeys don't transmit credentials, making them useless to an attacker even if intercepted.
At most, an attacker might gain access to the public keys stored in the database. Since these can't be used to reverse-engineer your private key, your account remains secure. If needed, you can simply revoke the old passkey and generate a new one.
The purpose of passkeys is to provide personal, identity-bound authentication – not shared credentials. But technically, yes, there are ways to share passkeys.
For example, Apple allows passkeys to be shared via AirDrop under certain conditions. You can also share passkeys by logging into the same password manager.
Yes. While passkeys offer a more secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional passwords, they aren't necessary – or even ideal – in every scenario. Here are a few examples:
Shared accounts
Passkeys are tied to you and your device. So for accounts shared among multiple people (like a shared Netflix account or business login), traditional passwords still work more flexibly – for now.
Enterprise or legacy systems
Older corporate systems, VPNs, or internal tools may not support passkeys at all – some industries move slowly when it comes to adopting new authentication tech.
Non-person entities (NPEs)
Developers using automated systems or scripts, they may need to authenticate to a server to perform tasks like scanning or data processing. In such cases, passkeys aren't practical. This could also extend to software needing to use authentication for secure API calls.
Additionally, there are environments where passkey adoption just doesn't fit yet. If you're on a device that lacks cloud backup or passkey syncing, such as an older smartphone or a public computer, it can be difficult or impossible to use passkeys effectively.
So while passkeys are the future of authentication, there are still valid reasons to stick with passwords in certain contexts – for now.
 CES 2025: Hands
CES 2025: Hands
 Webb telescope stares at our galactic neighbor, sees spectacular view
Webb telescope stares at our galactic neighbor, sees spectacular view
 NASA spacecraft flies right through sun explosion, captures footage
NASA spacecraft flies right through sun explosion, captures footage
 Google ditches continuous scroll in search results, brings back good old pages
Google ditches continuous scroll in search results, brings back good old pages
 Creators talk accessibility and building inclusive spaces at VidCon 2025
Creators talk accessibility and building inclusive spaces at VidCon 2025
 NYT's The Mini crossword answers for June 27
NYT's The Mini crossword answers for June 27
 NASA spacecraft zooms to new asteroid after dropping capsule on Earth
NASA spacecraft zooms to new asteroid after dropping capsule on Earth
 A government shutdown means bad news for Fat Bear Week
A government shutdown means bad news for Fat Bear Week
 Nishioka vs. Alcaraz 2025 livestream: Watch Australian Open for free
Nishioka vs. Alcaraz 2025 livestream: Watch Australian Open for free
 Webb telescope just made tantalizing find on ocean world Europa
Webb telescope just made tantalizing find on ocean world Europa
 How Creators for Palestine raised $1.6 million for Gaza — and what it means for the future
How Creators for Palestine raised $1.6 million for Gaza — and what it means for the future
 A government shutdown means bad news for Fat Bear Week
A government shutdown means bad news for Fat Bear Week
 NYT's The Mini crossword answers for June 27
NYT's The Mini crossword answers for June 27
 We tried Sony's new XYN headset: a game
We tried Sony's new XYN headset: a game
 Tesla reveals Cybertruck has sold more than DeLorean
Tesla reveals Cybertruck has sold more than DeLorean
 Here's how Google thinks AI should be regulated
Here's how Google thinks AI should be regulated
 Zoom transitions to AI
Zoom transitions to AI
 How to unblock Xnxx for free
How to unblock Xnxx for free
 Elon Musk says he will defy CNN, let creators stream the presidential debate on X
Elon Musk says he will defy CNN, let creators stream the presidential debate on X
GoPro's new Hero 5 action cameras make it easier to create epic videosWhy pressure cookers make such deadly explosive devices'Sound of Music' actress Charmian Carr dead at 73Congressman after New York bombing arrest: 'You are welcome Colin Kaepernick'Emmys 2016: Amy Schumer wears stunning tampon to the EmmysInterview: 2Dawn Games on its upcoming shooter 'Ravaged' and life as an indie studioBritney Spears dances like no one on Instagram is watchingJoe Biden announces major new steps in his fight for better cancer research'The People vs. O.J. Simpson' wins Emmy for Limited Series, just about everything elseHarry Potter's childhood home can now be yours — for a priceJoe Biden announces major new steps in his fight for better cancer researchHow Black Lives Matter made the leap from social media to social actionJapanese cosplayer poses with a live octopus for a photoshootFarewell flower crowns, it's all about face flowers nowHuawei nova and nova plus: MidCongressman after New York bombing arrest: 'You are welcome Colin Kaepernick'Extremely chill celebrity Kristen Bell ate pizza at the Emmys'Sound of Music' actress Charmian Carr dead at 73Elon Musk plans to go beyond Mars, says spacecraft needs new nameHere's the message Jimmy Kimmel's mom stuffed in those bagged Emmys snacks March Madness canceled, MLB, NBA, NHL, MLS, XFL seasons suspended due to coronavirus Hero Saoirse Ronan got Ed Sheeran to tattoo his own misspelled song title on his body Shared bikes, e Intense video shows oblivious truck driver drag a car with someone in it 'Pokemon Go' just made it easier to play at home during coronavirus pandemic Tesla eyes U.S. city for new Cybertruck factory Trump announced Google's coronavirus test site. That was news to Google. Guy goes on date with former manager of Olive Garden and posts breadstick intel to Twitter AMC, Regal cut down theater attendance because of coronavirus Trump says Google is making 'tremendous progress' on a coronavirus website How HBO's 'The Outsider' differs from the book The guy behind that viral hand Orlando promises the future of self The science march is about 'hope' for a fact Disney's live Downloading Zoom for work raises employee privacy concerns Freshen up your WFH digs with World Market’s 30% off furniture sale People still like United Airlines more than Donald Trump Tag Heuer's new smartwatch is ludicrously expensive Donald Glover just surprise dropped his new album on a secret website
3.3567s , 10209.9921875 kb
Copyright © 2025 Powered by 【Laruan】,Evergreen Information Network